Fiber Optic vs Ethernet Cabling: Pros, Cons, and Use Cases
When setting up a new network, one question always comes up: Should you use fiber or Ethernet cables?
Both carry data. Both connect devices. But they don’t perform the same. And they don’t serve the same needs.
If you’re building for speed, distance, or future upgrades, your cabling choice matters.
Here’s a simple comparison to help you make the right call.
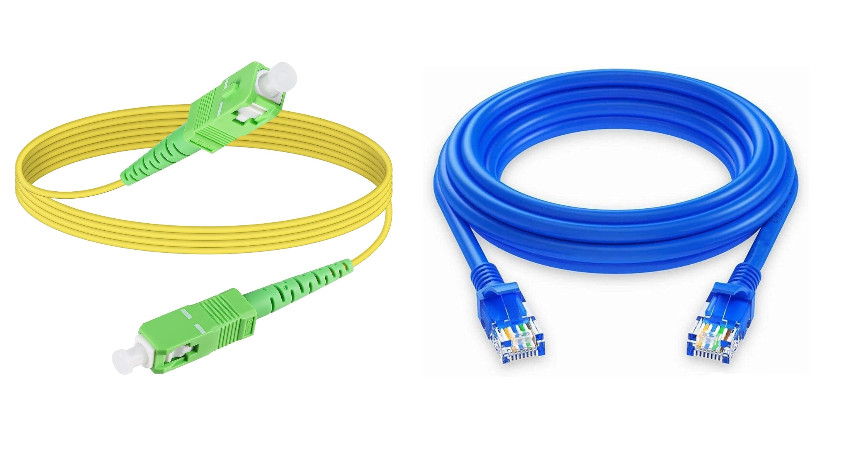
What’s the Difference?
- Fiber optic cables use light to carry data through thin glass or plastic strands. They support long-distance and high-speed transmission.
- Ethernet cables (like CAT5e, CAT6, or CAT6A) use electrical signals through copper wires. They’re common in offices and homes.
Fiber Optic Cables: Pros and Cons
✅ Pros
- Longer distance
Fiber can carry data over kilometers without loss. Perfect for multi-building setups or linking the far ends of a warehouse. - Higher speed potential
Fiber supports speeds of 1 Gbps to 100 Gbps and beyond. - No interference
Since data moves as light, fiber isn’t affected by electrical noise from nearby power lines or machines. - Better future-proofing
You can install fiber today and upgrade your hardware later without redoing the cabling.
⌠Cons
- Higher installation cost
Fiber cables and tools cost more upfront. Technicians need special training and splicing equipment. - Fragility
Fiber strands are thinner and more delicate than copper. They need careful handling and protection during installation. - Longer install time
Fusion splicing and termination take more time than crimping Ethernet connectors.
Ethernet Cables: Pros and Cons
✅ Pros
- Lower cost
Ethernet cables are cheaper and easier to install. Most electricians and IT teams know how to work with them. - Quick to deploy
You can terminate and test Ethernet cables on-site with basic tools. - Good for short distances
CAT6 and CAT6A support up to 10 Gbps within 55–100 meters, depending on the cable quality. - More flexible
Ethernet works well in small offices, shops, or homes without high-speed or long-distance needs.
⌠Cons
- Limited distance
Performance drops beyond 100 meters. Beyond that, you need repeaters or switches. - Signal interference
Nearby electrical sources can distort signals in Ethernet cables. - Lower long-term potential
You may need to re-cable if your speed or bandwidth needs grow quickly.
Which One Should You Use?
That depends on what you're building.
✅ Use Fiber Optic When:
- You're connecting buildings across a compound
- You need high-speed backbone links
- You want to reduce latency for large amounts of traffic
- You're installing CCTV systems over long distances
- You’re planning for 10 Gbps or higher future speeds
Example:
A hospital in Karen used fiber to link three separate blocks. Now they share medical records and camera feeds without delays.
✅ Use Ethernet When:
- You’re wiring a home, shop, or small office
- Your devices are within 100 meters of the switch
- You want a simple setup with low costs
- You don’t expect massive bandwidth needs
- You're running a local network for regular internet use
Example:
A 12-person office in Ngong used CAT6A for all internal devices. The setup took two days and worked perfectly for video calls and printers.
Can You Mix Both?
Yes. Many modern setups use both fiber and Ethernet.
- Fiber for the main connection between buildings or floors
- Ethernet for devices inside each room or office
You just need media converters or switches that support both types.
Final Thought
Don’t pick a cable just because it’s faster or cheaper. Pick what works for your space, your goals, and your users.
Talk to your technician. Walk through the layout. Think about future changes.
Then build a network that supports your work, not just today, but for years to come.